Effect of Tannins From Leaves of Cupressus Sempervirens Plant against Bacteria Causing Wounds and Burns Inflammations

Suadad Abdul-Elah Mohammad * 1,
Inaam Noori Ali 2,
Eman Mohammad Kadhim1, Intsar Kareem Kadhim 3
1- Industrial Applications and Materials Technology Research Centre – Department of Medical and Pharmaceutical Chemistry Research and Technology – Scientific Research Authority – Ministry of Higher Education
2- Environmental, Water and Renewable Energy Research and Technology Centre – Department of Environmental Research and Treatments – Scientific Research Authority – Ministry of Higher Education
3- Planning and Follow-up Department
Email: Swddalbasy@gmail.com
Abstract
Cypress is a genus of the Cupressaceae family, and its scientific name is Cupressus. The most important species is the Mediterranean cypress. This plant contains volatile oils such as pinene, cedrol, and camphor, as well as the active ingredient tannins and alkaloids. It has fifteen species, and modern medicine has found that cypress is used as an ointment, and when taken internally, it is used to treat coughs, colds, sore throats, and as an antispasmodic. It has been used since ancient times to treat dysentery and heal wounds. The most important species are: Cupressus bakeri, Cupressus arizonica, and Cupressus sempervirens.
The active substance (tannins) was detected in the leaves of the cypress plant using a 1% ferric chloride detector, which gave a dark green colour as evidence of positive detection. The extraction was carried out using polar solvents such as ether and ethyl alcohol at a concentration of 95%, and then the extract (tannins) was dried at a temperature of 40°C. Different concentrations were prepared to study the biological effectiveness against bacterial isolates, which are represented by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria, which cause wound and burn infections.
The Wells method was used to conduct a sensitivity test for the tannin extract, and the diameter of the inhibition zone was measured in millimetres for each isolate, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value was determined in milligrams/ml. The highest inhibition zone was 22 millimeters at a concentration of 300 mg/ml, and the MIC value was 150 milligrams/ml for Staphylococcus bacteria, and the highest inhibition zone for P. aeruginosa bacteria was 11 millimeters at a concentration of 300 mg/ml, and the MIC value was 150 mg/ml.
Keywords: Cypress plant, Tannin extraction, Bacteria.
استخلاص التانينات من اوراق نبات السرو ودراسة تاثيرها ضد البكتريا
المسببة لالتهاب الجروح والحروق
د.انعام نوري علي
2 مركز بحوث وتكنولوجيا البيئة والمياه والطاقات المتجددة – قسم البحوث والمعالجات البيئية – هيئة البحث العلمي – وزارة التعليم العالي
سؤدد عبد الاله محمد
Swddalbasy@gmail.com
إيمان محمد كاظم
1مركز بحوث التطبيقات الصناعية وتكنولوجيا المواد – قسم ابحاث وتكنولوجيا كيمياء المواد الطبية والصيدلانية – هيئة البحث العلمي – وزارة التعليم العالي
انتصار كريم كاظم
قسم التخطيط والمتابعة
الخلاصة :
نبات السرو هو جنس يتبع الفصيلة السروية والاسم العلمي له Cupressus من اهم انواعه سرو البحر الابيض المتوسط.يحتوي هذا النبات على الزيوت الطيارة مثل pinene,cedrol,camphen كذلك المادة الفعالة التانينات والقلويدات .وله خمسة عشر نوعا والطب الحديث وجد ان نبات السرو يستعمل كدهون وعندما يؤخذ داخليا يستعمل لعلاج السعال والزكام والتهاب الحلق ومضاد للتشنجات.ويستعمل منذ القدم لعلاج الزحار والتئام الجروح.من اهم انواعه: Cupressus bakeri,Cupressus arizonica,Cupressus sempervirens.
. تم الكشف عن المادة الفعالة (التانينات) في اوراق نبات السرو باستعمال كاشف كلوريد الحديديك تركيز 1% واعطى لون اخضر غامق دليل الكشف الموجب وتم الاستخلاص باستعمال مذيبات قطبية مثل الايثر والكحول الاثيلي يتركيز 95% ، و من ثم تم تجفيف المستخلص (التانينات) بدرجة حرارة 40 م° . وحضرت منه تراكيز مختلفة لدراسة الفعالية البايولوجية ضد العزلات البكتيرية والتي تتمثل بالبكتريا العنقودية الذهبية Staphylococcus aureus والبكتريا الزنجارية Pseudomonos aeruginosa المسببة لالتهابات الجروح والحروق.
استخدمت طريقة الحفر wells لاجراء فحص الحساسية لمستخلص التانينات وتم قياس قطر منطقة التثبيط بالمليمتر لكل عزلة وحددت قيمة التركيز المثبط الادنى MIC مقدرة بالمليغرام/مللتر وكانت اعلى منطقة تثبيط 22 مليمتر عند التركيز 300 ملغرام/ مللتر وقیمت MIC 150 ملغرام/مللتر للبكتريا العنقودية واعلى منطقة تثبيط للبكتريا الزنجارية هي 11 مليمتر عند التركيز 300 ملغرام / مللتر وقيمة MIC 150 ملغرام/مللتر.
الكلمات المفتاحية : نبات السرو ، استخلاص التانينات ، البكتريا
Introduction
Cypress scientific name Cupressus Sempervibens L. belongs to the cypress family Cuphessaceae and English name Eng. Cypress is an evergreen tree, 10-30 meters tall, very dense branches, scaly leaves, crossed and overlapping triangular shape, unisexual flowers, monoecious, cypress is spread in the regions of the Eastern Mediterranean and southwest Asia and is naturally spread in Iran, Turkey, the Mediterranean region and Morocco. The ancient Greeks used it to treat some diseases such as azithromycin, asthma and cough. The part used is the female cones and young leafy branches (Aziz et al,2023)
The fruits are known as Gla bulus and are collected for medical use when they are green and are used as a vasoconstrictor and to stop bleeding.
It contains a volatile oil that contains terpenes and their derivatives, and catechol tannin. The young branches of the cypress contain a volatile oil obtained by distillation and used in the treatment of whooping cough (Hamza,2022). The plant contains many medically important chemical components such as alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes, volatile oils and tannins (Azzaz et al,2019) and plays an important role as an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory. The plant is considered antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiparasitic, anti-insect, anti-cancer and wound-healing (Harfouch et al,2022; Koriem,2009)
Importance of the research: Finding a plant drug from the cypress plant (leaves) to treat skin inflammation caused by bacteria that cause wound and burn infections.
Research problem: Trying to find the inhibitory activity of the tannin extract of cypress leaves against the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa that cause wound and burn infections.
Research methodology: Detection of the active substance tannins by extracting and diagnosing them using HPLC. Especially the compound (Jannic acid), then different concentrations of this extract were made to study its effect against staphylococcus and aeruginosa bacteria using the Wells drilling method and comparing the two isolates in terms of resistance and sensitivity to the extract. By measuring the diameter of the inhibition zone and determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), then analysing the data and finding significant differences using the statistical analysis method. (ANOVA)
Research limits: Then the research was conducted in the laboratories of the Department of Research and Technology of Medical and Pharmaceutical Chemistry – Scientific Research Authority – Ministry of Higher Education. Date of work: January 2021 – October 2021.
Research hypotheses: We assume that the active ingredients in the cypress plant have inhibitory activity against bacteria, so the focus is on the substance (tannins) because they are astringent and at the same time antibacterial.
Previous studies:
Recent studies indicate that cypress plants are effective against bacteria, viruses, parasites, insects, anticancer and wound treatment (Al-Shafi et al,2016)
Objective of the research: The research aims to extract the active substance (tannins) from the leaves of cypress trees and identify Tannic acid. And study the effect of the plant extract at different concentrations against the bacteria pseudomonas, Staphylococcus aureus, that cause wound and burn infections. And determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for each bacterial isolate and determine the resistance and sensitivity of each isolate to this extract.
Materials and methods
1 – plant:
We got the plant (Cupressus) from the garden of the Ministry of Science. And diagnosed depending on (Encyclopedia of Life, 2013).
Leaves were washed and dried at (35±2) ℃, and saved in plastic sacs.
2- Chemical materials:
Chemical materials as Ferric chloride, Ethanol 99%, and Ether from the laboratories of the department.
3- Laboratory equipment:
Equipment used, such as Rotary evaporation and oven (40℃). To get rid of liquids and humidity while (HPLC to diagnose taninic acid.
4-cultures :
It was used for nutrient agar, nutrient broth. (LAB) . To grow and save bacterial isolates and perform sensitivity tests.
5-Bacterial isolates;
The isolates of bacteria were taken from inflammation of wounds and burns, and it was diagnosed in the laboratory of the medical centre.
- Staphylococcus aureus causes inflammation of wounds and burns.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes inflammation of wounds and burns.
Methods
- Detection of tannins :
We detect tannins by using ferric chloride (1%), prepared aqueous extract from leaves of Cupressus weighing 5 g in 50 ml of distilled water. The solution was filtered and then boiled, and after that, the filtrate solution was added to the reagent in (equal ratio. Green colour (dark or blue-green) was the positive result.(Mohammad &Al-Sammaraie,2021)
- Preparation of tannic extract:
Depends on the Harbon method to get tannins by using polar solvents as ether. We took 500 g from the leaves of the plant and put it in solvent ether at (60-80) ℃ to remove pigments and fats. After that, we added ethanol (99%) for 48hr. The solution was filtered and concentrated by rotary evaporator to get brown sediment finally. The product was added to water at (80-100) ℃ to complete the extraction process. A stereer was used for (48) hr., then the solution was concentrated another time to get brown sediment and dried by oven (40℃). We calculated the weight to be used, then prepared the concentration from dried weight mg/ml(Mohammad & Al-Sammaraie,2021)
- Diagnosis of taninic acid.
Tannic acid was diagnosed by HPLC and compared with standard solution at 6.3 retention time, wavelength 254 nm and used column (Id 250*4.6).
- Sensitivity test:
Agar well diffusion method was used by micropipette (0.3 ml) half dilution (300,150, 75,37.5) mg/ml and the well control, which represents distilled water only for comparison petri dish was incubated at (37) ℃ for (24) hr. After that, the diameter of the inhibition zone was measured.(Elgailani&Ishak,2016)
- Statistical analysis:
The results were analysed by ANOVA test. According to the laboratory experiments for explaining the effects of tannic extract against the bacterial isolates were explained. The probability of 0.05 is a significant or non-significant difference for the extract.
Results and Discussion
After detection for tannins by ferric chloride 1% reagent, we found a dark green colour, which is a positive result, as Figure (1)
| Figure (1): Dark green color refers to the positive reaction of to diagnose tannins.
Extraction and purification identified tannic acid by (HPLC) at wave length 25nm, retention time 6.3 comparison with standard solution figure (2).
|

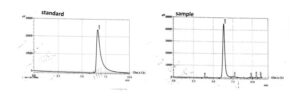
Figure (2): Appearance of tannic acid in the HPLC device with wavelength 254 nm and 6.3 retention time compared with a standard solution.
Sensitivity tests to the plant extract by using half dilution (300, 150, 75, and 37.5 mg/ml.
Staphylococcus aureus showed a higher inhibition zone (22 mm, while pseudomonas aeruginosa showed (11 mm at 300 mg/ml for both bacteria. Table (1).
|
Bacteria isolates |
Concentration of plant extract mg/ml | Control | |||
| 300 | 150 | 75 | 37.5 | Distilled water | |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
22
a |
12
b |
– | – |
6 c |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 11
a |
9
b |
– | – |
6 c |
Table (1): The diameter of the inhibition zone in mm for 2 isolates of bacteria that were treated with many concentrations of plant extract.
Number 6 indicates that there was no inhibition zone around the well and the control distilled water.
- Different letter means a significant difference among concentrations and control at a probability of 0.05 was found.
- MIC value for staphylococcus aureus 150 mg/ml to the pseudomonas aeruginisa.
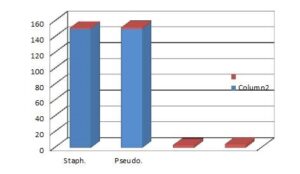
Figure: (3) MIC value (mg/ml) for two types of bacteria: S: Staphylococcus aureus, P: Pseudomonas aeruginosa

Figure 4); photo of inhibition zone ( mm) for
(2) Isolates from bacteria at different concentrations from the plant extract (Cupressus).
- C control (distilled water.
- S staphylococcus aureus .
- P pseudomomus aeruginosa .
- 300, 150, 75, and 37.5 mg/ml different concentrations of plant extract.
There were many studies dealing with the (Cupressus) plant for different types as Cupressus sempervirens, especially volatile oils that were extracted from fruits and leaves, including α-pinene, careen, it were found active against bacteria as (Staphylococcus aureus, E.coli, Bacillus ) and against yeast (candida albicans) so bacteriostatic, fungistatic. (Emami et al,2006)
Another study of volatile oil isolated from fruit and leaves of Cupressus plant against 5 isolates of bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus ). It was found that MIC value (100 mg/ml ). Most types of bacteria use agar wells. (Othman et al,2019) Also, another search showed that volatile oils affected bacteria and yeast (Candida) by the disc method. Results showed that the volatile oil was an antioxidant, too. (Zoughi et al,2015)
So they studied the activity against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, E. coli for the ether extract of Cupressus and pinean and the results showed no activity against Candida. (Elgailani&Ishak,2016 ). Statistical analysis for cupressus) showed (0.7%) al keloids, (0.22%) flavonoids, 0.31 tannins, 0.06 phenols, 1.9% saponins and some volatile oils(Al-Shafi,2016). There are very important medicines used to suppress. (Selim et al,2014). The volatile oils of the cypress plant gave high efficacy as antioxidants, antibacterial and insecticides (Sriti et al,2023).
There was a search for Algerian cupressus sempervirens leaf extracts against phytopathogenic bacteria. Aureus, a pectobacterium causative agent of soft rot on potato, Solanum tuberosum and three clinical bacteria, Stains (Staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca). Ethanolic Acetone and aqueous extracts. We were investigated. For their phenolic content.. The results revealed that all extracts possessed varying antibacterial activities against the tested organisms. Gram +ve and Gram -ve bacteria, and Pectobacterium (Ialeff et al,2021). Another study about Cupressus sempervirens fruit extracts, in Ethanolic extract, was conducted. Staphylococcus aureus and Porphyromonas gingivalis at various concentrations, where the diameter of the inhibition Zone. For Staphylococcus at a higher concentration was 15 mm) and the diameter of the inhibition Zone for Porphyromonas was (22 mm), Water extract had no effect on bacteria except Staphylococcus, where the inhibition Zone was (14 mm). For E. coli bacteria, neither extract had any effect. Also, the effect of C. Sempervirens fruit extracts was revealed as anticancer properties against HT 29 colon cancer cells and Mcf7 breast cancer cells (Salah,2022)
In vivo toxicological evaluation of essential oils exhibited a concentration-dependent manner with a lethal (LC50) equal to 6.6 Mg/ml. For Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus bacteria in Zebra fish, (Akermi et al,2022) Antimicrobial activity was found using different hydrosol concentrations. (10-20% µ/V) for Cupressus leylandii, showing the potential of the tested. Hydrosols inhibit microbial growth. of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus
and Candida albicans (Almedia et al,2024). The major compounds of the essential oil (citronell and terpinene) showed strong interaction with the active Site of the bacterial DNA gyrase enzyme. Explaining the antibacterial mode of action of the essential oil and ciprofloxacin was also used. For the docking Study was found that the essential oil of Cupressus funebris causes bacteria. Membrane. Rupture. dreet (Helo&Yuan,2023). Cupressus arizonica fruit ethyl extract in 100% concentration. inhibits different species of bacteria. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) on E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus was 12.5 mg ml, while Salmonella SP was at 50 mg/ml. (Nayyef et al,2023)
Conclusions
The study (in vitro) explained that the leaves of the plant extract of the tannic acid was active against gram +ve bacteria as Staphylococcus aureus and gram-ve bacteria as Pseudomonous aeruginosa causing wound and burns inflammations at (300) mg/ml, the result courage using leaves of the plant as treatment for bacterial inflammations as wounds and burns inflammations.
Recommendation
Extraction and purification of volatile oils from the fruits and flowers of Cupressus plant, and study of antimicrobial activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi
REFERENCES
- Akermi, S.; sma Qui , S.; Sma Qui, S.; Elhadef, K; Fourati, N.(2022)Cupressus sempervirens .Essential oil. Exploring the Antibacterial Multitarget Mechanisms: Chemo-potential Toxicity Prediction. And Safety Assessment in Zebra fish Embryos, Molecules, 27(9): 2630
- Al- Shafi , A . E.(2016) Medical importance of Cupressus sempervirence-Areview. IOSRJ. pharm ., 6(2),66-76
- Almedia 2 His; Crugenia, Jil; Amanal, J.S; Rodrigues, A.E.(2024) Disclosing the potency of Cupressus leylandii A. B. Jacks & Dalim, Eucalyptus globulus Labill, Aloysia cithodora palau, and Melissa officinalis hydrosols as eco-friendly. Antimicrobial agent, Natural products and.. Bioprospecting. 14 (1):24
- Aziz,R.A. Agha,M.A. Qawas,M. Qarbisa, M. S. Bilal, A.B. et al. (2023) Atlas of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants in the Arab World, League of Arab States – Arab Centre for the Studies of Arid Zones and Dry Lands, Damascus, p. 301
- AZZaZ, N.A. Hamed. S.S., Talaat, A, K.(2019) Chemical Studies on cypress leaves (Cupressus sempervirens) and their activity as antimicrobial agent. Al-Azhar Journal of Agricultural Research.(AJAR ) 44 ( 2 ) : 100 – 109
- Elgailani, I.E. A and Ishak, C.Y.(2016) Methods of Extraction and Characterisation of Tannins from Some Acacia species of Sudan Pak. J. Anal. Enviru, chrm. 17 (1): p. 43-49
- Emami,S.A;ASILI,J.;Rahmizadeh,M.;Khayat,H.H(2006).Chemical and Antimicrobial Studies of Cupressus Semipervirens. L. and C. horizontalis Mill.Essential oils.I.J.Ph.S., 2(2),103-108
- Hamza, A.M.(2022) Global Medicinal Plants, Description – Components – Methods of Use and Cultivation, pp. 227-228
- Harfouch, R.M , Barakat,A. . Chouman,F. and a Elshimali,Y.(2022) Antibacterial Effect of Essential Oil Extracted from Cupressus machocarpa Leaves against Several Strains. International Journal of Pharmacognosy (IJP) vol 109, No. 6: 123-126,
- Helo, X. and. Yuan, C.(2023) Antibacterial mechanism of action and in silico molecular docking Studies of cupressus funebris essential oil against resistant bacterial strains. Heliyon. Vol. 9, cell.com/heliyon.
- Ialeff, K. A ; Debib, A; Menadi, S.• Alsaɣadio M., et al,(2021) phenolic content and Antibacterial Activity of cupressus sempervirens Leaves Extracts Against phyto Pathogenic Bacteria. pecto bacterium atho Septicum causative. Agent of Soft Rot on potato and clinical bacteria. Strains, Trop. J. Nat. Phod. Res. 5(5); 866-872
- Koriem,K.M.M.(2009)Lead toxicity and the protective role of cupressus sempervirence RevistaLatino American.De Quimica., 37(3),230-242
- Mahammad, J.M. and. AL-Summariae, O.K. (2021). Evaluation of the efficacy of tannins and flavonoids isolated from pomegranate peels on some liver and kidney functions in local mice. Sammanna J. Pune. App). Sci. 3(2) : 1−11
- Nayyef, S. H.; Abdul Wahab, M.H; Ahmed, N.M, and Hassan, M.O. The Effect of Cupressus arizonica Fruit Ethyl Alcoholic Extract on Some Bacterial Species that were isolated. From different Infections of the Human Body’s sites. IOP. Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2023.
- Othman, L.; Sleiman, A.; Abdelmaseh, R.M.(2019)Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols and Alkaloids in Middle Eastern Plants. F. Microbiol.,10:911,
- Salah, H.(2022) Antibacterial and Anticancer activity of Cupressus Sempervirens L. fhult extraction. MSG, thesis in Applied Industrial Technology. Alquds university
- Selim, S.; Adam, M.E; Hassan, Sh.M.(2014) Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of the essential oil and methanol extract of the Mediterranean cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) .C.A.M.,14:179
- Sriti, J.; Salem, M.; Wannes, W. and Mejri, H.(2023) Antioxidant, antibacterial and insecticides activities of cupressus(cupressus sempervirence L.) essential oil. Int. J. Env. H. Res.,41(1)
- Zouaghi, N.;Bellel,Ch.;Cavalerio,C(2015).Identification of volatile compounds, antimicrobial properties and antioxidant activity from leaves, cones. And stems of cupressus sempervirencefrom Algeria.A.J.M.Res.,9(2),83-90